ToC
- P1. two sum
- P2. longest consecutive sequence
- P3. container with most water
- P4. 3sum
- P5. trapping rain water
- P6. longest substring without repeating characters
- P7. median of two sorted arrays
- P8. find all anagrams in a string
- P9. subarray sum equals k
- P10. reverse nodes in k-group
- P11. edit distance
- [P12. ]
记录一些刷到的算法题的解法。
P1. two sum
很简单的一道题但是发现在做的时候其实有一些需要注意的地方
unordered_mapinstead ofmap,因为map底层是红黑树,查询效率是O(logn),而unordered_map底层是哈希表,查询效率是O(1)(worst case O(n))unordered_map[key]如果key不存在,会返回0,但是有情况是0是有效值,所以需要用find判断是否存在
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
std::unordered_map<int, int> m;
for (int i = 0, n = nums.size(); i < n; i++) {
if (auto p = m.find(target - nums[i]); p != m.end()) {
return {i, p->second};
}
m[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {-1, -1};
}
};
P2. longest consecutive sequence
两个特点:
- 如果\(x-1\)存在,那么\(x\)一定不是最长连续序列的起点,跳过
- 如果\(x-1\)不存在,那么\(x\)一定是最长连续序列的起点,开始向后查询连续序列的长度,更新最大值
class Solution {
public:
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // use a set
int ans = 0;
for (auto num : s) {
// if we have (num - 1) in the set,
// num will not give us the answer.
if (s.find(num - 1) != s.end()) {
continue;
}
// this inner loop will run only n times,
// which gives us a time complexity of O(n)
int i = 1;
while (s.find(num + i) != s.end())
i++;
ans = std::max(ans, i);
}
return ans;
}
};
P3. container with most water
把下标\(i, j\)围成的容器的盛水量设为\(m(i, j)\),有
\[m(i, j) = \min(x_i, x_j) * (j - i)\]有(\(x_1, x_2, ..., x_{n-1}, x_n\)),目前双指针位于\(x_1\)和\(x_n\),设\(x_1 < x_n\),那么有
\[m(1,n) = x_1 * (n - 1)\]同时
\[m(1, n-1) = \min(x_1, x_{n-1}) * (n - 2)\] \[\le x_1 * (n - 2)\] \[< x_1 * (n - 1)\] \[< m(1, n)\]所以每次都应该移动较小的那个指针,直到两个指针相遇。
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int i = 0, j = height.size() - 1;
int ans = 0;
while (i < j) {
int current = std::min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i);
ans = std::max(ans, current);
if (height[i] < height[j]) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
P4. 3sum
- 三重循环,排序之后,枚举\(a\),在\(a\)之后枚举\(b\)和\(c\),使用双指针优化
- 需要去重,跳过重复的\(a\),\(b\)即可
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// duplicated
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
// don't put this inside the loop below
// otherwise it's not a two pointers but
// a time complexity of O(n3)
int k = n - 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
// duplicated
if (j != i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
continue;
}
while (j < k && nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] > 0) {
k--;
}
// all following j will not satisfy
if (j == k) {
break;
}
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0) {
ans.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
P5. trapping rain water
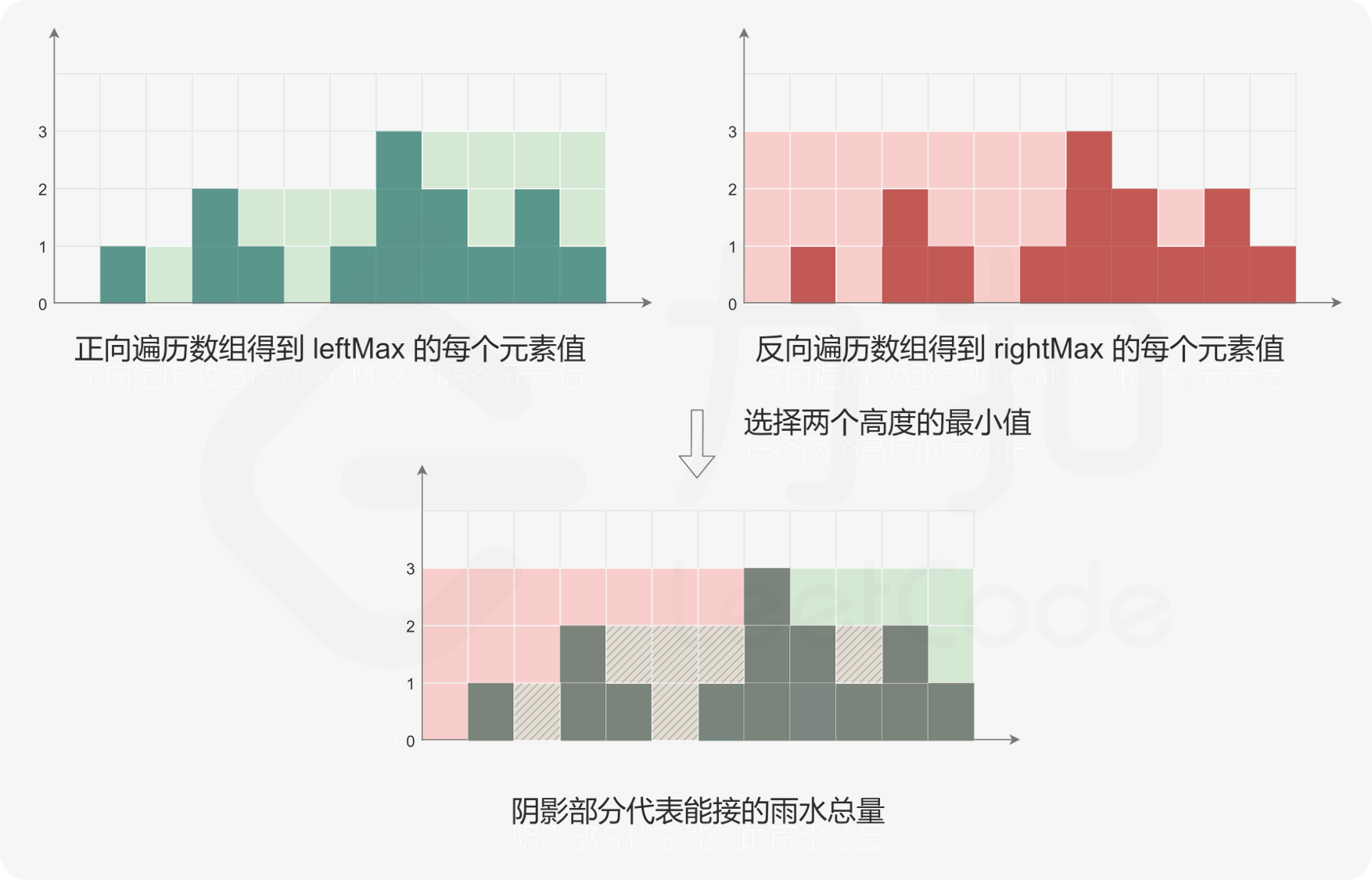
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
vector<int> forward(height.size());
vector<int> backward(height.size());
int ans = 0;
int m = 0;
// 正向计算每个下标处最多能接多少水
for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); i++) {
m = std::max(m, height[i]);
forward[i] = m - height[i];
}
m = 0;
// 反向计算每个下标处最多能接多少水
for (int i = height.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
m = std::max(m, height[i]);
backward[i] = m - height[i];
// 最终答案是每个下标处按两种方式计算后最多能接水的最小值
ans += min(backward[i], forward[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
P6. longest substring without repeating characters
P7. median of two sorted arrays
P8. find all anagrams in a string
- 对每个字母进行计数,然后记录当前窗口中字母数量和p中字母数量不同的字母的数量,如果不同的字母数量为0,那么说明当前窗口是一个anagram,记录答案。
- 注意在移动窗口时,如果移出的和移入的字母是相同的,那么判断值是否为0会被判定两次,因此需要分别判断(代码的注释)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string p) {
unordered_map<char, int> counts;
vector<int> ans;
int diff = 0;
if (p.size() > s.size()) {
return {};
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {
counts[s[i]]++;
counts[p[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
if (counts[i] != 0) {
diff += 1;
}
}
if (diff == 0) {
ans.emplace_back(0);
}
for (int i = p.size(); i < s.size(); i++) {
counts[s[i]]++;
if (counts[s[i]] == 0) {
diff -= 1;
} else if (counts[s[i]] == 1) {
diff += 1;
}
// 不能写在循环开头,因为删掉的和新增的可能是同一个字符
counts[s[i - p.size()]]--;
if (counts[s[i - p.size()]] == 0) {
diff -= 1;
} else if (counts[s[i - p.size()]] == -1) {
diff += 1;
}
if (!diff) {
ans.emplace_back(i - p.size() + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
P9. subarray sum equals k
刚开始想用双指针,但是写出来问题比较多,看题解才看到前缀和+哈希的解法,前缀和也不需要存数组,只需要一个变量即可。
class Solution {
public:
int subarraySum(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int pre = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> m;
m[0] = 1;
int ans = 0;
for (auto num : nums) {
pre += num;
ans += m[pre - k];
m[pre] += 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
P10. reverse nodes in k-group
- 每次翻转k个节点,递归剩下的节点
- 或者,使用一个额外数组存储然后翻转
P11. edit distance
- 对于两个字符串\(s_1\)和\(s_2\),分别有对字符串\(s_1\)或\(s_2\)进行插入/删除/替换操作,一共是6种情况,而实际上对\(s_1\)进行删除操作就等价于对\(s_2\)进行插入操作,因此最后的情况是:对\(s_1\)进行插入操作,对\(s_2\)进行插入操作,对\(s_1\)进行替换操作。一共三种。
- 对于字符串如”adadh”和”dah”,以及”adadh”和”da”,前者至多比后者操作次数多一次。
- 也就是说,对于字符串\(s_1\)的前\(i\)个字符和字符串\(s_2\)的前\(j\)个字符,编辑距离最多是前\(i\)个字符和前\(j-1\)个字符的编辑距离+1,前\(i-1\)个字符和前\(j\)个字符的编辑距离+1,前\(i-1\)个字符和前\(j-1\)个字符的编辑距离+1,取最小值。 4.
[P12. ]
##